In 1959, an expedition of historians unearthed an exquisitely carved ancient statue of Gautama Buddha from the island of Thoddoo.
Buried under slabs of stones, possibly to protect it from being demolished along with the the temples following the Islamization of the Maldives in 1153 AD, the statue was a priceless archaeological find.
Before long, however, the island was gripped with controversy. ‘The religion of worshipping statues has begun!’, some islanders were described as saying, according to the book ‘A New Light on the History of Maldives’.
One early dawn soon after its discovery, the ancient statue was found decapitated by vandals.
The statue was then taken to Male’ and displayed at Mulee’aage, the current Presidential residence. Before the week had ended, another mob barged in and smashed it to pieces leaving behind just the serenely smiling head, which is now displayed in the National Museum in Male’.
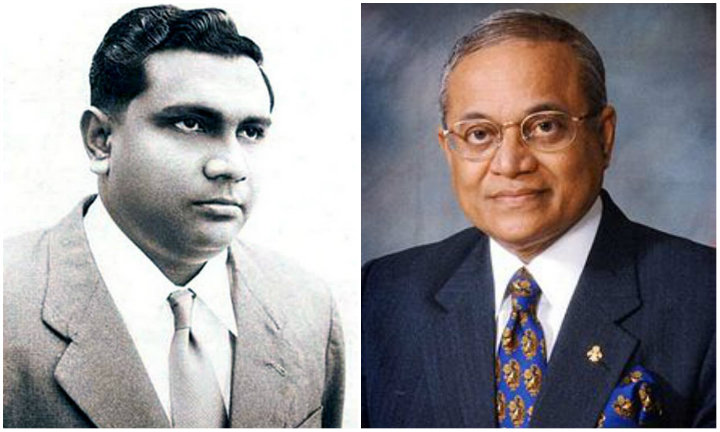
The Prime Minister at the time, strong-man Ibrahim Nasir, who didn’t hesitate to personally lead gunboats to forcefully depopulate the island of Thinadhoo following the southern rebellion, knew better than to investigate the vandalism.
It was simply pointless, because half a century later, unidentified vandals would proceed to smash, burn and destroy the SAARC-gifted monuments in Addu, for allegedly being ‘idols of worship’.
The State vs. the Tolerant
Just like Nasir, the modern Maldivian politician knows better than to challenge the deep-rooted fear of ‘other religions’ that is so firmly ingrained in the Maldivian psyche.
On the other hand, it makes for a great political gimmick.
Quite tellingly, the ruling party, seven opposition parties and a network of 127 NGOs are all planning to protest on December 23 in order to renew their vows against allowing ‘other religions’ in the Maldives.
It seems a rather redundant cause, considering the 2008 Maldivian constitution already forbids non-Muslims from becoming citizens, and mandates that the nation remain 100% Sunni Muslim.
This status quo, however, was recently challenged by a group of Maldivians who gathered in Male’ on December 10, on the occasion of the International Human Rights Day, in silent protest against the lack of religious freedom in the Maldives.
The sit-down protest was disrupted within minutes by a violent gang, leaving one man with serious injuries to the head.
Joining the chorus of local politicians eagerly latching onto the controversy, “Reeko” Moosa, the former MDP Parliamentary Group leader, demanded the prosecution of those who called for ‘religious tolerance’ – otherwise considered a positive phrase elsewhere in the world.
Independent journalist and blogger, Ismail Hilath Rasheed, who was among the freedom advocates, has been taken into police custody.
Meanwhile, the National Security Committee in parliament has decided to summon participants of the protest, citing their duty to defend Islam and uphold the country’s constitutionally imposed religious unity.
It is abundantly clear that there’ll be no debate on the subject, and that at the heart of it lies the holy writ of country’s unchallengeable Constitution.
The immutable constitution
Thomas Jefferson, one of the great founding fathers of America, once proposed that the American constitution should be rewritten every 20 years, lest the dead end up ruling over the living.
There are, of course, excellent reasons to deliberately make it difficult to modify a country’s constitution, not the least of which is to protect it from whimsical rulers.
In this regard, however, the Maldives goes one step further than the rest.
Speaking about the incarceration of Hilath Rasheed, Police Sub-Inspector Ahmed Shiyam said “Calling for anything against the constitution is illegal”.
There appears to be a general consensus among lawmakers and the public alike that the constitution is beyond all criticism, and any dissenting word spoken against it should be considered a grievous crime.
This would perhaps imply that the entire Chapter 12 of the constitution is now utterly redundant, for what good is a chapter on amending the constitution when apparently it is illegal to find any fault with the existing one?
One presumes that President Nasheed himself must now be put in chains and dragged before the courts for blasphemously uttering in July 2010 that he was in favour of a Parliamentary democracy, whereas the holy constitution explicitly decrees a Presidential system.
Thankfully, other democracies of the world recognize that obeying the constitution doesn’t necessarily mean agreeing with it.
In neighboring democracies like India, writer activists such as Booker Prize winning author Arundhati Roy write fiery articles openly defying the State, and major political parties publicly campaign to remove specific Constitutional clauses they have philosophical differences with.
In a true representative democracy, the public is generally free to advocate and lobby their representatives for causes they believe in.
In the past few weeks, it has emerged that Maldivian public apparently doesn’t have this freedom.
The other sacred text
Perhaps, then, it is not the Constitution, but Islam that imposes certain limits on the debate?
Unfortunately, in the Maldives, there is no way to tell apart the limits imposed by Islam from the ones imposed on it.
It appears that many Maldivians are convinced that the ultra-conservative Adhaalath Party and their Salafi cousins are the foremost authorities on the subject of Islam in the known universe.
But for that to be true, one must argue that every other Islamic nation in history has been wrong.
While one Maldivian blogger has been languishing in a prison cell for the past week for advocating religious tolerance, there is an abundance of Imams, caliphs and even a certain Prophet from history who seem to be in agreement with that blogger’s opinion that Islam does indeed have room for religious tolerance.
Didn’t the Prophet himself say, “Whosoever does injustice to a protected non- Muslim, then I will be his enemy (on the Day of Judgement)”?
The Cairo Declaration on Human Rights in Islam, drafted by the Organisation of the Islamic Conference as a Shari’ah compliant alternative to the UDHR, declares the right of people to a dignified life free of discrimination on the grounds of religious belief, among other things.
Maldivian scholar Dr Abdulla Saeed of Melbourne University, argues in his book ‘Freedom of Religion, Apostasy and Islam’ that there is “a vast amount of clear Qur’anic texts in favour of freedom of religion”.
Needless to say, his book was banned in the Maldives.
The burden of defining ‘true Islam’, instead, fell on a small group of short-sighted conservative political Mullahs working out of a Ministry building in Male’. And in their opinion, Islam forbids the mere mention of ‘other religions’ – despite what the Qur’an says.
‘Because we’re special’
12th century copper plate grants found in the Maldives reveal the blood-soaked, painful process of conversion of the Maldives to Islam. The Sultans of the day went through the trouble of bringing in Buddhist monks and beheading them in the capital.
The modern day Maldives takes a much simpler route. The 2008 Constitution unilaterally declares all Maldivians to be Sunni Muslim without the courtesy of so much as an opinion poll.
Maldivians in general are quite proud of the ‘100% Muslim’ statistic that is frequently bandied about.
But it raises a few fundamental questions that are nevertheless extremely taboo in the Maldivian society.
At what point of Maldivian history has there ever been a public census on religion?
Does the Maldivian state even have the right to unilaterally declare a citizen’s beliefs? Which other Islamic State or Empire in Islam’s 1400 year old history has taken this liberty – and under whose authority?
Those We Do Not Speak Of
A cursory look at online Social networks easily proves the existence of several non-Muslim Maldivians, and Dhivehin who appear to not subscribe to a religion at all.
If we were to do the unthinkable and disregard the holy constitution for just a minute, how morally justified is it really to make their mere existence a crime potentially punishable by death?
Consider the fact that our very economic survival depends on treating other non-Muslims – those who are non-related by blood, culture or language – with generous hospitality.
Does this radical notion of unilaterally enforced Islam only apply to those born of Dhivehi parents? Could the Parliament conceivably declare tourists and other visitors also to be Sunni Muslims while within Maldivian territory?
At what point does the whole affair begin to sound absurd?
Chaos theory
Politicians of both major parties argue that introducing the freedom of conscience to minorities would result in chaos and disorder in society, much like introduction of democracy did with the introduction of political rights. But are any of these politicians sincerely willing to return to the non-chaotic days of the past when they were jailed for simply expressing an opinion? If not, why not?
The Maldives has been “100% Muslim” since at least the Gayoom days. So why do we not see the utopian fantasy of a prosperous, peaceful, gentle society of fellow Muslims treating each other with kindness?
Instead, it appears that Maldivian lawmakers and government no longer have to talk about roads or health or food or development, for they now have the one dead horse of religion to flog for all eternity.
Is it really that hard to see there’s something wrong with the picture when eight political parties – both the ruling and the opposition – plan to rally in order to “defend Islam” against each other?
Which Islamic principle was being followed by the MPs who tried to force their way to the International airport in an effort to remove a banner depicting the region’s cultural diversity?
Presumably, it takes a tremendous amount of will power for these lawmakers to restrain themselves from forcing their way past security into the National Museum to destroy the still intact head of the ancient coral-stone idol of the Thoddoo Buddha that our ancestors had failed to destroy.
What Islamic value lies behind the sort of blood lust that drives an ordinary Maldivian to go and violently attack a fellow Maldivian simply for being a non-Sunni Muslim?
Based on what Islamic criteria do we religiously uphold certain parts of the Shari’ah penal code such as flogging, while completely disregarding others such as amputating limbs, or stoning half-buried humans to death?
These are all important, crucial questions. But until there’s room for an honest debate, how would we ever find out?
End of Reason
“I disapprove of what you say, but I will defend to the death your right to say it”, wrote S.G. Tallentyre in 1906, in a quote widely misattributed to French philosopher Voltaire.
Over a century later, we Maldivians have yet to appreciate the sentiment behind this powerful phrase.
While jihadist literature with fiery, cataclysmic titles are openly sold in Salafi bookshops around the capital, the slightest spark of reason is immediately stamped out by an unthinking brigade of conservative clerics and opportunistic politicians.
The broken, still smiling Buddha in the National Museum bears witness to our long history of stubbornly refusing to accept reason.
But today, more than ever, it is necessary to ask difficult questions and face hard facts, because the line that marks where the debate stops also marks the point where, as Thomas Jefferson feared, we become enslaved to the past.
All comment pieces are the sole view of the author and do not reflect the editorial policy of Minivan News. If you would like to write an opinion piece, please send proposals to [email protected]
Likes (2)Dislikes
(2)Dislikes (0)
(0)